
| MERIS Level 1 Radiometric Processor - Radiometric Recalibration Algorithm Specification | 
|
The impact of the radiometric calibration changes was assessed by comparing RR products processed with 2nd reprocessing and 3rd reprocessing configuration. FR products in 3rd reprocessing configuration were not available at time of the analysis. A method was developed to correct 2nd reprocessing Level 1 products to 3rd reprocessing quality.
MERIS standard processing algorithms are revised, and as part of this, the degradation model of the calibration diffuser has been improved, which results in updated gain values per detector. This is applied in L0 to L1 processing. The Reduced Resolution products are currently undergoing a reprocessing (3rd reprocessing) at ESA; however, this applies only to archived RR products, and the Level 1b FRS in use at the MERIS user community are at 2nd reprocessing quality. A method has been developed reverting the second reprocessing gains and applying the 3rd reprocessing gains, so that TOA radiances are comparable with the 3rd data.
The gains of the 2nd and 3rd reprocessing are taken from MERIS auxiliary files RAC (RAdiometric Calibration) files. The RAC files can be found at the following ESA websites: MERIS Auxiliary Data Files of 2nd reprocessing MERIS Auxiliary Data Files of 3nd reprocessing
The radiometric calibration as described below is a non-linear process including several steps. The radiometric gains are the second last step before the L1b are written. However, the last step is the stray light correction which is a non-linear process and not revertible from L1b product. The recalibration is therefore only an approximation.
The valid MERIS samples are digital counts resulting from the detection and acquisition by MERIS of a bi-dimensional field of spectral radiance in front of the instrument. The objective of the radiometric processing, together with the stray light correction, is to estimate that spectral radiance. An inverse model of the MERIS processing is used for that purpose, using parameters stored in the Characterisation and Radiometric Calibration data bases and the MERIS samples themselves. The MERIS acquisition model may be described as:
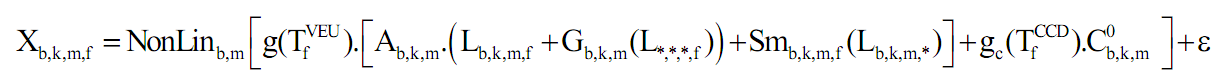
Where
This model is inverted during processing: The inverse of the absolute instrument gain ALb,k,m is applied to the valid samples of all bands after dark and smear signal subtraction, with a compensation for the estimated temperature which is expressed as a function of time:
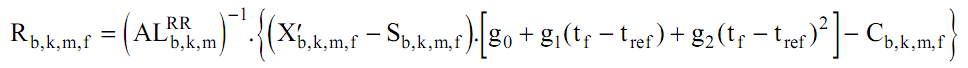
Where Rb,k,m,f are the spectral radiances before the straylight correction. The inverse of the 2nd reprocessing radiometric gains (AL) are multiplied to R, and then the gains of the 3rd reprocessing are multiplied to give an estimate of the 3rd reprocessing radiances.