
| SMAC - Algorithm Specification | 
|
Algorithm Specification of the science processors of the MERIS/(A)ATSR Toolbox
SMAC is a Simplified Method for Atmospheric Corrections of satellite measurements. It is a semi-empirical approximation of the radiative transfer in the atmosphere. The signal at the satellite is written as the sum of the following components, which are then expressed in simple analytical terms:
To give an example, the spherical albedo, S, is expressed as a function of the aerosol optical depth at 550nm:
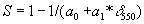
where a0 and a1 are parameters which need to be determined for a given spectral band and aerosol model. These parameters can be retrieved by a best-fit against a full radiative transfer model. The well establish 6S code was used for this purpose.
With this technique the radiative transfer in the atmosphere can be computed much faster than with a full model. A comparison has shown that the gain in computation time is several hundred times in comparison with the full model (see reference below. Here the comparison was made with the predecessor 5S). However, numerous coefficients have to be determined in advance from best-fits with a full numerical model. Also, changes in the spectral band characteristics require new coefficients. The accuracy of the SMAC approximation in comparison with 5S is generally better than 3% difference between the TOA reflectances.
The practical application of such a simplified model is to invert the radiative transfer equation, and to calculate the surface reflectance from satellite measurements. Because of its "speed", this method is best suited for application to large data volumes.
The SMAC requires as input, in addition to the measured top of atmosphere radiances, the surface pressure, the ozone content and the water vapour content, and, most important, the aerosols. SMAC has also implemented these in a very useful way. Aerosol, for example, requires the selection of an aerosol model and the aerosol optical depth at 550nm. The SNAP implementation gives the user the choice to select the MERIS meteorological data for pressure, ozone and humidity.
The algorithm is described in "SMAC : a simplified method for the atmospheric correction of satellite measurements in the solar spectrum" H. RAHMAN, G. DEDIEU Int. J. Remote Sensing, 1994, vol.15, no.1, 123-143.